[Editor’s note: This is a guest post originally by Kevin Browne Follow @hamiltonkb. The post was originally published on Software Hamilton. It provides an incredible overview of the softeware culture and scene in Hamilton and how it is different and distinct from Toronto.]
Hamilton’s software industry had great years in 2011 and 2012. I meant to write an article looking at the future of the industry since the 2012 review article. I ended up dumping a bunch of related thoughts about Hamilton and the software industry more broadly into this super long article. Here goes…
Our industry is larger than it ever has been, with continued growth already in 2013 as firms hire new employees and new firms startup. Your Hamilton Biz ran an article the other week covering the surge in software startups in Hamilton. Innovation Factory saw an elevenfold increase in software startups as clients in the 2 years from 2010 to 2012, from 6 to 66. Software Hamilton’s job board saw a 400% increase in the number of job postings from 2011 to 2012. Software as an industry in Hamilton is growing, and we can now begin to quantify that growth.
It might be early, but I think we can start to ask ourselves what a software industry in Hamilton means. What could a software industry do for Hamilton? What could Hamilton do for the software industry? And how do we get there? The industries of a city tend to specialize based on geographical or institutional strengths. Even though you can write code anywhere, software industries tend to specialize too. I don’t think it’s an accident that an accounting software startup like Freshbooks sprang out of a financial center like Toronto. So I’ll start by talking about Hamilton.
Hamilton
Hamilton is proud of its identity and history. We like to mythologize ourselves even. The French explorer Robert de La Salle was the first European to set foot in Hamilton in August 1669, where he prophesied that “here one day there shall be a great city”. This prophesy came true for Hamilton – first as the ambitious city in the 19th century, and then as the steel city in the 20th century. Hamilton gained its ambitious city moniker for its can-do attitude in the face of adversity. We never give up, we work hard, and we do great things that influence the world in a positive way. An expansive manufacturing sector provided much of this influence on the outside world, creating half the steel for Canada by end of World War 2.
Manufacturing and steel underwent a decline in the latter half of the 20th century that was felt by cities across North America. We lost many industrial employers over the years. Stelco alone went from 14,000 workers in the 1980s to less than 1,000 today. Actor Jim Carrey used to look across the bay from Burlington growing up and think “this is where the great jobs are”. Now instead Hamilton has serious problems with poverty as documented by the Code Red series. There is a 21 year difference in life expectancy between our best and worst neighbourhoods, with 90k below the poverty line (including 10k full-time workers!), and 18.5k people using food banks (including 8.5k children!!). I know that poverty isn’t unique to Hamilton and that “think of the children” is cliche enough to be done by The Simpsons. But seriously, think of the children relying on food banks… it’s completely appalling.
Poverty is just one of the problems. We’ve got environmental problems like Randle Reef and air pollution / smog. We’ve got health problems like asthma and obesity. Many of these problems exist in other cities or even in all cities, but often they are measurably worse in Hamilton. A lot of these problems are also connected to one another when you dig deeper. When Hamilton’s manufacturing sector declined it made many of these problems a lot worse.
The decline of Hamilton’s manufacturing sector mirrored the decline in its stature more broadly. For a long time Hamilton was actually considered a sister city to Toronto. Check out this 1957 promotional film about Mississauga’s development, where Hamilton is identified as such. Herbert Rogge predicted in a speech to the Hamilton Chamber of Commerce in 1954 that Hamilton would become “the forward cleat in a ‘golden horseshoe’ of industrial development from Oshawa to the Niagara River”, coining the term Golden Horseshoe in the process.
Great cities impact the world around them, they act as centers of job creation with gravity that pulls in from around them more than they are pulled themselves. When Hamilton lost its manufacturing clout we failed to keep up with the world around us, and in the process lost some control of our own destiny and our relative ability to impact the world around us. With healthcare and education emerging as the top employers, important (i.e. funding) decisions impacting employment in Hamilton are now being made at Queen’s Park instead of towers at King and James. It’s all enough to make people anxious about what kind of future Hamilton has as a city.
 There’s been some talk lately of Hamilton becoming Toronto’s Brooklyn. Toronto itself is booming in population and clout, with more high-rise buildings under construction than anywhere in North America. A new Go Station is opening up in 2015 with all day train service to Toronto. Instead of being a great place to work, Hamilton could end up becoming a great place to live while commuting to a job in Toronto. It makes me think of the Brooklyn Bridge, which opened in 1883 when Brooklyn was an independent city, before being absorbed by New York in 1898. As they saw the Brooklyn Bridge rise up, did their city fathers realize that Brooklyn was about to be annexed? Combinations of internal problems and external forces have felled civilizations and empires, let alone cities. Is this just the end of Hamilton as a city? No longer Toronto’s sister within the Golden Horseshoe, but instead its suburb within the GTA?
There’s been some talk lately of Hamilton becoming Toronto’s Brooklyn. Toronto itself is booming in population and clout, with more high-rise buildings under construction than anywhere in North America. A new Go Station is opening up in 2015 with all day train service to Toronto. Instead of being a great place to work, Hamilton could end up becoming a great place to live while commuting to a job in Toronto. It makes me think of the Brooklyn Bridge, which opened in 1883 when Brooklyn was an independent city, before being absorbed by New York in 1898. As they saw the Brooklyn Bridge rise up, did their city fathers realize that Brooklyn was about to be annexed? Combinations of internal problems and external forces have felled civilizations and empires, let alone cities. Is this just the end of Hamilton as a city? No longer Toronto’s sister within the Golden Horseshoe, but instead its suburb within the GTA?
And yet and yet. There’s been talk for decades about Hamilton experiencing a renaissance, and it appears to finally be coming to fruition. While education and healthcare might not be able to fill Hamilton’s private sector jobs hole, they have put a nice bottom on Hamilton’s decline that has prevented us from facing problems at the scale of cities like Detroit. Hamilton has only experienced jarring stagnation, not total collapse. Politically there is now an active and engaged citizenry generating and advocating for new ideas in areas like urban revitalization and job creation (or at least, ideas that are new to Hamilton). At the grassroots level the art community has led a broader creative sector revival downtown, with the super crawl and art crawl being the most visible of many achievements. There’s more cranes in the sky downtown than anytime in years. There is a growing sense that something is happening in Hamilton, and that this time the renaissance is more than talk. That said, the private sector jobs hole, poverty, and other problems remain significant problems. While a software industry alone can’t return Hamilton to its former glory, it is a critical piece of the puzzle.
Software Industry
Why is software such a critical industry? Because software is eating the world, as discussed by Marc Andreesen,
“My own theory is that we are in the middle of a dramatic and broad technological and economic shift in which software companies are poised to take over large swathes of the economy. More and more major businesses and industries are being run on software and delivered as online services—from movies to agriculture to national defense.”
Software industry Yoda-figure Paul Graham believes that this is a trend with “decades left to run”. In the past software meant operating systems, spreadsheets, wordprocessors, and video games. The early Internet added accessing information and e-commerce to the mix. But now the Internet and software are everywhere. We have an Internet of things where our phones, cars, TVs and other devices all contain fairly powerful computers connected to the Internet. As a result software is now used to create and consume content for industries like television, movies, photography, and books. Software didn’t just kill Blockbuster, it made Netflix and many other new empires.
 Far from being too late for Hamilton to get in the game, we’re really only at the beginning of the disruption. We can look forward to other major disruptions like self-driving cars and entire homes being built by 3D printer technology. Two of the biggest areas of the economy that will be disrupted are healthcare and education, for example by apps that can diagnose conditions like skin cancer. Increasingly software isn’t about building a layer of technology itself like an operating system or developing a new algorithm, but building a solution that solves a problem out in the world.
Far from being too late for Hamilton to get in the game, we’re really only at the beginning of the disruption. We can look forward to other major disruptions like self-driving cars and entire homes being built by 3D printer technology. Two of the biggest areas of the economy that will be disrupted are healthcare and education, for example by apps that can diagnose conditions like skin cancer. Increasingly software isn’t about building a layer of technology itself like an operating system or developing a new algorithm, but building a solution that solves a problem out in the world.
It doesn’t end there either. In non-software STEM fields, software is playing a larger role. Science is increasingly reliant upon computer simulations of complex system to make advances. Whether it’s predicting global warming, creating customized drugs, or exploring how the brain works, chances are software played a role to organize all the data or compute patterns. All of these devices collecting data has led to a whole lot of data! Big data has become a field focused on capturing, retaining and analyzing all this data for useful purposes. Governments are collecting all this data too, and they are now beginning to open this data up to the public as part of the Open Data movement. This data can similarly be analyzed and used to create new kinds of helpful apps.
There’s a virtually limitless frontier of possibilities for software to improve the human condition in the century ahead.
This frontier of possibilities is now accessible for everyone to explore too. The Internet of things means that software itself can be delivered from anywhere to anywhere. In the 19th century we had seaports and in the 20th century we had airports. In the 21st century every device is becoming a “softwareport” from which goods and services can be imported and exported.
The number and quality of jobs created by the software industry is well documented. Mobile device app stores alone created 500,000 new jobs in America by 2012. The software development jobs created by this industry provide salaries that go beyond a living wage to living well. The industry creates more than software developer jobs, as software development firms require administration, management, marketing, legal and everything in between.
These software developer jobs are also accessible in that the educational requirements are reasonable in time and cost. Learning how to program through traditional institutions like Universities and Colleges is the route most follow, but it has never been easier to learn using alternative options. Organizations like Ladies Learning Code, HackerYou and Bitmaker Labs are offering in-person courses next door in Toronto that can allow you to become a web developer in as little as 9 weeks. Websites like Khan Academy, Codecademy and Coursea allow you to learn how to program online at no charge.
Hamilton Software Industry?
It’s easy to see how a software industry can be great for Hamilton. While we have many problems, the biggest is the lack of jobs. The software industry is booming with jobs, not just in other cities, but right here too. These jobs are both very accessible in terms of educational requirements and they are high-paying too. And for those that aren’t computer programmers themselves, the industry also creates a plethora of spin-off jobs. They offer an opportunity for us to influence the world and become a center of gravity again, as software is the driving force behind the rapid changes so many industries are experiencing.
The greatest thing is that it’s already happening right now. Within a generation Hamilton could employ tens of thousands of people in this industry to replace the losses we’ve experienced in manufacturing.
What I think might be less obvious but no less important is what Hamilton can do for a software industry. Hamilton might have many problems, but software startups thrive when they solve problems. Often times in Hamilton we look for political solutions to problems. This is because sometimes a more top-down government-executed political solution is required. A startup company can’t change public infrastructure for example. But thinking about how to solve these problems with new technology and startup businesses can help us create new jobs and wealth.
Getting There
These are a few preachy thoughts in no particular order on how Hamilton can get there. I’m a fan Brad Feld’s Startup Communities, and I’ve spent a lot of time looking at how other communities like Waterloo and Toronto made it happen there. I’m sure a lot of these ideas aren’t my own, but things I’ve picked up through osmosis at this point.
 1) We aren’t going to be (or beat) Silicon Valley
1) We aren’t going to be (or beat) Silicon Valley
Sometimes people will say to me, “so you want Hamilton to become like Silicon Valley”. I want Hamilton to have prosperity like Silicon Valley, but we’re not going to become Silicon Valley, or any other startup ecosystem for that matter. That’s because for the most part we can’t beat them at their own game. How hard would it be to beat Google at web search, or Adobe at graphics editing? Silicon Valley, New York, Toronto, Waterloo and every other ecosystem has carved their own path to success. Trying to become them or compete against them isn’t the best approach. It’s not to say that firms in Hamilton can’t compete against firms anywhere in the world, it’s just that our best returns on investment are going to come from exploring completely new areas in the universe of possible startups, rather then fighting over a slice of the exact same pie. Hamilton should focus on the things we can do better than anywhere else in the world. We can create our own game that the rest of the world can’t beat us at. And on that note…
2) Turn Hamilton’s problems into our advantages
All of these problems that we have in Hamilton have potential for startup ideas inside of them somewhere. Education and healthcare alone are gold mines. There are apps for everything from alcoholism to apps that let you shop green to apps aimed at preventing suicide. If there’s a problem you’re passionate about in Hamilton, chances are there is a way that software can help solve that problem not just locally, but everywhere.
3) Take advantage of Hamilton-specific strengths
We have a world class medical school in town. Mohawk College is making a big push into mHealth with their new MEDIC centre and AppsForHealth.
We also have a burgeoning arts community. Video games need everything it has to offer – storytellers, artists, animators, musicians, etc. We can also sell crafts and other art online. Lookout for an upcoming event being planned with Etsy Canada to help do just that.
Taking what industries work well in Hamilton already and “electrifying” aspects of them with software so that we can sell goods and services to a world market is a promising approach.
4) Have patience
Building a software industry in Hamilton will be a decades long process. It generally takes years to start companies, build products, gain traction in the market, wade through growing pains and pivots, get funding, scale the companies, train a workforce, develop veterans within the workforce, etc. Look at a company like Ottawa’s Shopify. Their problem was identified in 2004, an initial personal-use solution was developed in months, the more scalable general-case solution Shopify itself wasn’t launched until 2006, wasn’t profitable until 2008, received millions in Series A funding in 2010 and Series B funding in 2011, and went from 40 employees to 100 between 2010 and 2012. A lot of these great things just don’t happen overnight.
5) Keep plugging away on community building
Innovation Nights, Startup Weekends, DemoCamps, Lunch ‘n Learns, StartupDrinks, IT meetups, hackathons, programming language user groups, technology user groups – all these different events galvanize and animate the community in different ways, providing value in terms of creating connections, education, PR, generating startups, and motivation/inspiration. A community isn’t a member organization, a club, an institution, or any particular series of events. The community is the network of connections between individuals, and these events enable those connections to form.
 I’m really happy to hear that the good folks at Brave New Code are working on bringing WordCamp to Hamilton in 2013. I hope that more people continue to take up new community building initiatives in the years ahead. A broad set of individuals and institutions organizing different events tends to indicate a healthy community. In particular I think there’s significant value in doing more hackathon, user group, and educational type events. If you’re interested in organizing events then find something you would like to do that’s missing in Hamilton, tell other people what you are doing, and then do what you have to do to make it happen. Don’t ask permission. Don’t take a vote. Don’t have a president or a treasurer. Don’t over structure it. Just start doing it.
I’m really happy to hear that the good folks at Brave New Code are working on bringing WordCamp to Hamilton in 2013. I hope that more people continue to take up new community building initiatives in the years ahead. A broad set of individuals and institutions organizing different events tends to indicate a healthy community. In particular I think there’s significant value in doing more hackathon, user group, and educational type events. If you’re interested in organizing events then find something you would like to do that’s missing in Hamilton, tell other people what you are doing, and then do what you have to do to make it happen. Don’t ask permission. Don’t take a vote. Don’t have a president or a treasurer. Don’t over structure it. Just start doing it.
You don’t need to organize events to community build. You can cheerlead and inform by blogging, podcasting, tweeting, informally mentoring, or giving a talk. You can open up your LinkedIn connection list to others – sometimes all it takes is knowing the right people. Be inclusive to anyone that wants to join the community. Introduce them to everyone that’s relevant to them. Help other people out with their own initiatives and ideas, and accept help with your own. Try to spend a portion of your time providing informal mentorship by sharing experience or knowledge, even if it’s only at events like Startup Drinks. Let yourself be mentored informally by others.
6) Beware of bad actors
“Any community built upon trust and mutual support is naturally vulnerable to the parasitic few who will exploit the goodwill of others.” – Diana Kander. I hesitate to even make this point. That’s because I’ve found 99.99% of the people in the Hamilton community have something positive to offer. Not everyone is going to play every role successfully, we all have our strengths and weaknesses. But it’s easy to see the good in everyone.
 Sometimes certain personalities just clash and people don’t get along or can’t work together. Sometimes founders break-up and there’s rough feelings. Sometimes an employee leaves and it isn’t amicable. The community in Hamilton is still fairly small. It’s in our best interests to try to avoid grudges, be understanding, give the benefit of the doubt, discourage gossip, and communicate openly as best we can. But when I say “bad actors” it’s not these situations I’m talking about. These things are a natural and even healthy outcome of different people trying to work together.
Sometimes certain personalities just clash and people don’t get along or can’t work together. Sometimes founders break-up and there’s rough feelings. Sometimes an employee leaves and it isn’t amicable. The community in Hamilton is still fairly small. It’s in our best interests to try to avoid grudges, be understanding, give the benefit of the doubt, discourage gossip, and communicate openly as best we can. But when I say “bad actors” it’s not these situations I’m talking about. These things are a natural and even healthy outcome of different people trying to work together.
When I talk abut bad actors I mean those who take more than they give, who are unethical, or who may even be a legitimate narcissist and/or a psychopath. The community tends to organically reject these people. Some are obvious, like the guy trying to sell “silver water” that he claimed cured cancer (??) at an event last year. Others are less obvious, they can be dishonest, misrepresentative and/or manipulative, and they can camouflage themselves with a good cause. It may sound crazy, but if you meet 1000+ people over a year or two of events you may find it’s an unfortunate reality. These bad actors are incredibly few and far between, and as a friend said, it’s best “to let nature find a way”. It’s not something to worry about, but to be aware.
7) Institutional support matters
I’m a grassroots guy in that I like the go out and make things happen approach. I think real change happens from the bottom-up. But institutions have a pivotal and necessary role to play. The post-secondary institutions act as talent generators. Innovation parks, regional innovation centers and economic development agencies catalyse growth with the services they offer. The institutions in Hamilton have been doing a fantastic job, especially over the last 5 years. It’s just that it needs to continue.
8) Worrying about a lack of funding or developers
Two of the biggest things I hear about from people getting off the ground is difficulty finding funding and/or developers. Finding developer talent is a matter of having money to hire good developers. Southern Ontario is full of them and our schools crank out more every year. I’ve found it extremely rare that non-technical founders have been able to find talent without paying them, but it does happen. I think I might write a blog post on this topic in particular.
If you need money for your startup there is a myriad of government programs that can help. Crowdfunding is now an option too. One of the most successful approaches in Canada has been bootstrapping. Find customers and accept their money in exchange for providing a solution to their problem. Desire2Learn was bootstrapped for a decade before receiving $80 million in funding in the largest VC investment ever for a Canadian software startup.
If you absolutely need funding from investors to get your startup off the ground, you can try local organizations like Angel One or GHVF. But you may ultimately have to make phone calls and get on a plane. Halifax’s GoInstant, which was sold for $70 million to Salesforce recently, was funded by investors in Silicon Valley. If you can’t find local capital willing to invest in your startup, you shouldn’t let that stop you.
Whatever the case these difficulties are expected and just problems to be solved, not some kind of “problem with Hamilton” in terms of ability to do a startup here. GoInstant made it work in Halifax, we should consider ourselves lucky that we’re in Southern Ontario with Toronto and Waterloo right next to us.
9) Embrace the region
And we are very lucky to be in Southern Ontario. Waterloo and Toronto have done an incredible job building startup ecosystems. They were both featured on the recent Startup Genome top 20 startup ecosystems list. On regional blogs there’s been a lot of talk lately about how Toronto and Waterloo are really the “same ecosystem”. Though he recognized Silicon Valley is of course more developed, Jesse Rodgers actually compared our region to Silicon Valley in a recent blog post. People are increasingly using the language “Ontario startup scene” as opposed to Waterloo or Toronto specifically. We should embrace the idea of a Southern Ontario ecosystem. If hiring experienced talent coming out of RIM in Waterloo and using marketing talent in Toronto can help you scale a startup in Hamilton, who cares? A win for one of the cities in this region is really a win for all of them. The only caveat I would add is that we shouldn’t let embracing the region stop us from being proud of doing what we do in Hamilton.
10) Grow, grow, grow, grow…

Companies are built by people. Software is written by people. The bottom line is that we need more people doing software and startups in Hamilton. There are a lot of initiatives that are animating the community at this point. I’d say 90-95% of the existing software companies in Hamilton are aware of the community and in the Software Hamilton directory now. A lot of energy has been spent gathering people together. But it can’t just become a fixed group of initiatives and people, it should be dynamic and expanding. The next step is engaging more new people, whether it’s Hamiltonians or pulling people in from outside Hamilton. Promoting software development as a career path, creating opportunities for more non-developers to learn software development, and creating opportunities for non-entrepreneurs to engage in the startup scene will all be key in the years ahead.
Taking The Long View
A software industry can build Hamilton’s 21st century Dofasco and Stelco. It can allow us to improve and impact the outside world in ways greater than we ever could before. It can help put Hamilton back on the map as a great city by building products that improve the way people live all over the world. It can create jobs that help wipe out poverty in this town. I know this is all pretty ambitious. It will take several decades of hard work and smart decisions from all of us here already and many, many newcomers joining us. But make no mistake that it can be done, and it will be too.





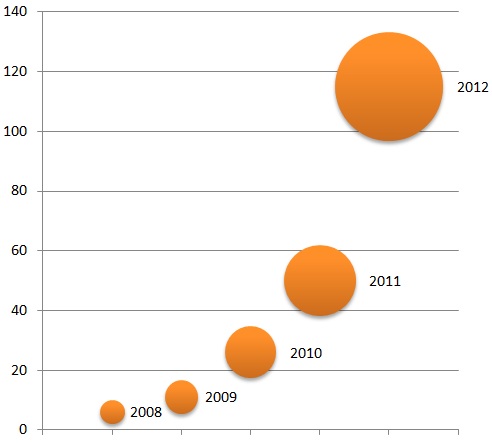 We have been committed to connecting high-tech entrepreneurs, companies and enthusiast. Two major vehicles for connecting the community are
We have been committed to connecting high-tech entrepreneurs, companies and enthusiast. Two major vehicles for connecting the community are